Cataract Surgery Techniques
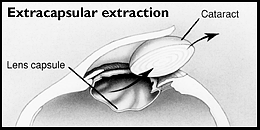
Using the extracapsular cataract extraction technique, the surgeon
makes an incision where the cornea and sclera meet. Carefully entering the eye
through the incision, the surgeon gently opens the front of the capsule and
removes the hard center, or nucleus, of the lens. Using a microscopic
instrument, the surgeon then suctions out the soft lens cortex, leaving the
capsule in place.
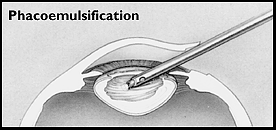
Phacoemulsification is a modification of the extracapsular cataract
extraction. In phacoemulsification, the nucleus is fragmented by an ultrasonic
oscillating probe. The nuclear fragments are simultaneously suctioned from the
eye. The size of the incision is smaller than the incision needed to remove the
capsule in the extracapsular technique.
 Phacoemulsification Technique - Animated (2.5 MB Quicktime
.mov)
Phacoemulsification Technique - Animated (2.5 MB Quicktime
.mov)
 Phacoemulsification Technique - Live (3.1 MB Quicktime
.mov)
Phacoemulsification Technique - Live (3.1 MB Quicktime
.mov)

An intraocular lens (IOL) is a clear plastic lens that is implanted in
the eye during the cataract operation. Lens implants have certain advantages.
They usually eliminate or minimize the problems with image size, side vision and
depth perception noted by people who wear cataract eyeglasses. They are also
more convenient than contact lenses because they remain in the eye and do not
have to be removed, cleaned, and reinserted.
 Intraocular Lens (IOL) Implantation. (2.0 MB Quicktime
.mov)
Intraocular Lens (IOL) Implantation. (2.0 MB Quicktime
.mov)
|